

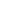
Since our inception in March 2012, we have been dedicated to the abrasives and polishing materials industry. Through 12 years of experience, we have honed our expertise in processing and sales, accumulating a wealth of knowledge in manufacturing and design. Our company is driven by a relentless pursuit of quality and innovation.
This commitment is reflected in our strict quality control standards and the use of advanced manufacturing technology in every product we produce. We are committed to exceeding your expectations and becoming your trusted partner in abrasives and polishing solutions.

YEAR OF EXPERIENCE

I've been using Dapeng Abrasive Materials edge banding buffing wheels for a few years now, and I'm consistently impressed by their quality. They leave a smooth, flawless finish every time, even on tricky projects. I also appreciate the company's commitment to innovation - they're constantly coming out with new products that make my work easier and more efficient. Overall, I highly recommend Dapeng Abrasive Materials for anyone looking for top-notch abrasives and polishing materials.


For years, we've relied on Dapeng Abrasive for premium quality abrasive materials. Their experience in the industry reflects in the durability and performance of their products. A trusted partner for all our abrasive needs.


Dapeng Abrasive's expertise has transformed our production efficiency and quality. With their strict quality control standards, we receive exceptional products every time. Professionalism and reliability make them our go-to partner." - DEF Manufacturing
